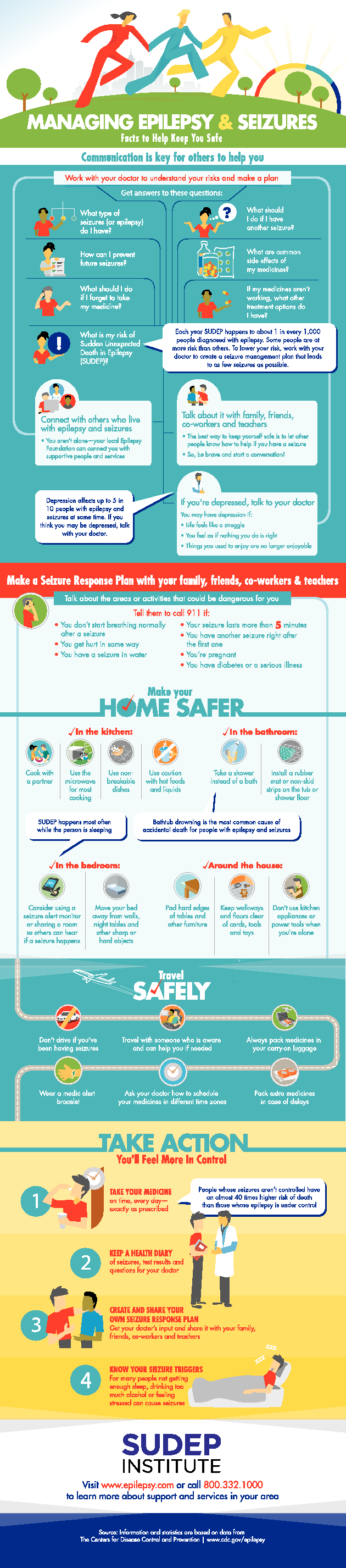
Managing Epilepsy & Seizures Infographic

Here's a PDF version you can print
Resources
Epilepsy Centers
Epilepsy centers provide you with a team of specialists to help you diagnose your epilepsy and explore treatment options.
Epilepsy Medication
Find in-depth information on anti-seizure medications so you know what to ask your doctor.
Epilepsy and Seizures 24/7 Helpline
Call our Epilepsy and Seizures 24/7 Helpline and talk with an epilepsy information specialist or submit a question online.
Tools & Resources
Get information, tips, and more to help you manage your epilepsy.